Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Vs Lynch Syndrome
Familial adenomatous polyposis vs lynch syndrome. Prophylactic surgery or treatment. Two major autosomal dominant forms of heritable CRC are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and Lynch syndrome also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Patients with a differential diagnosis of attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis FAP vs.
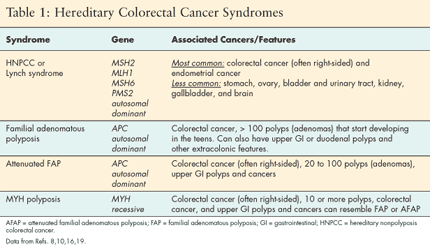
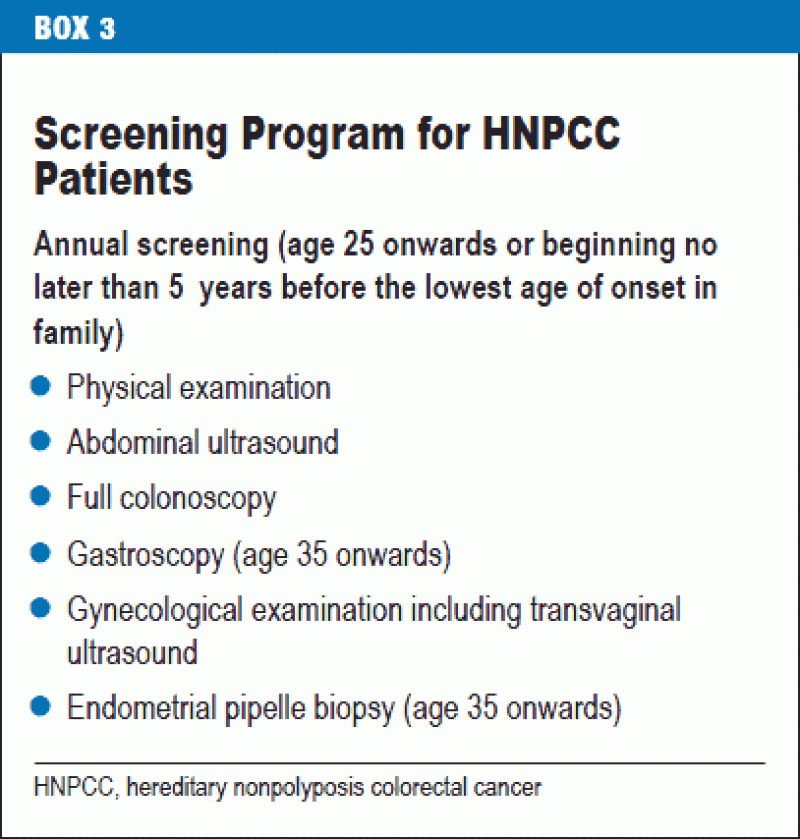
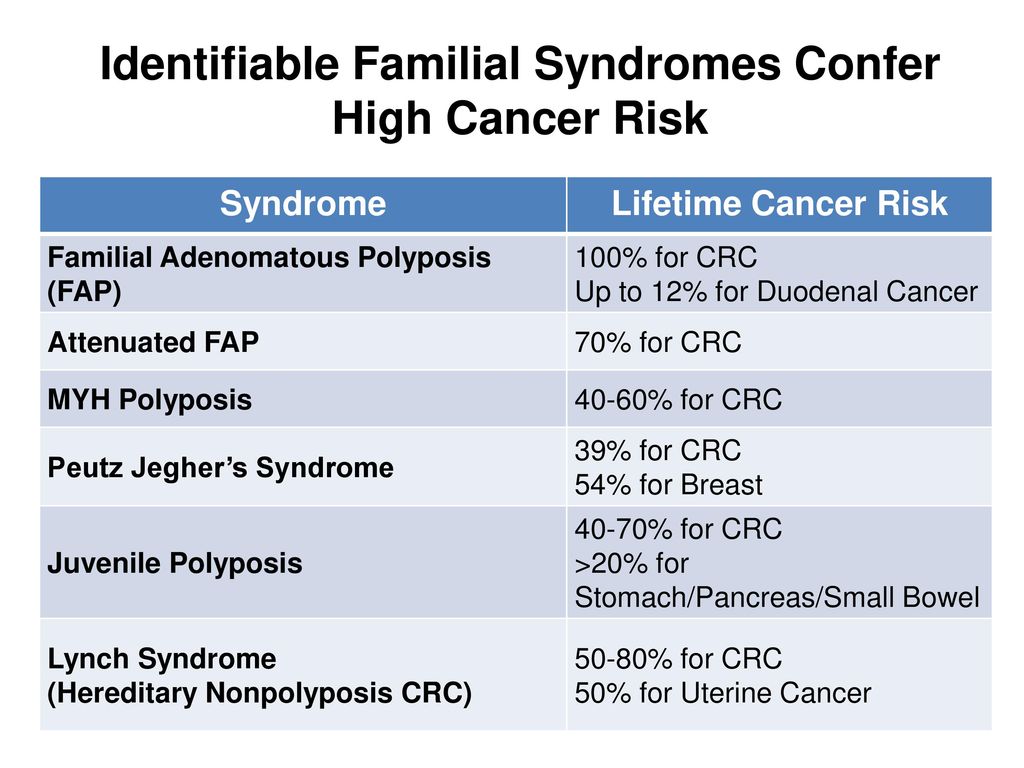
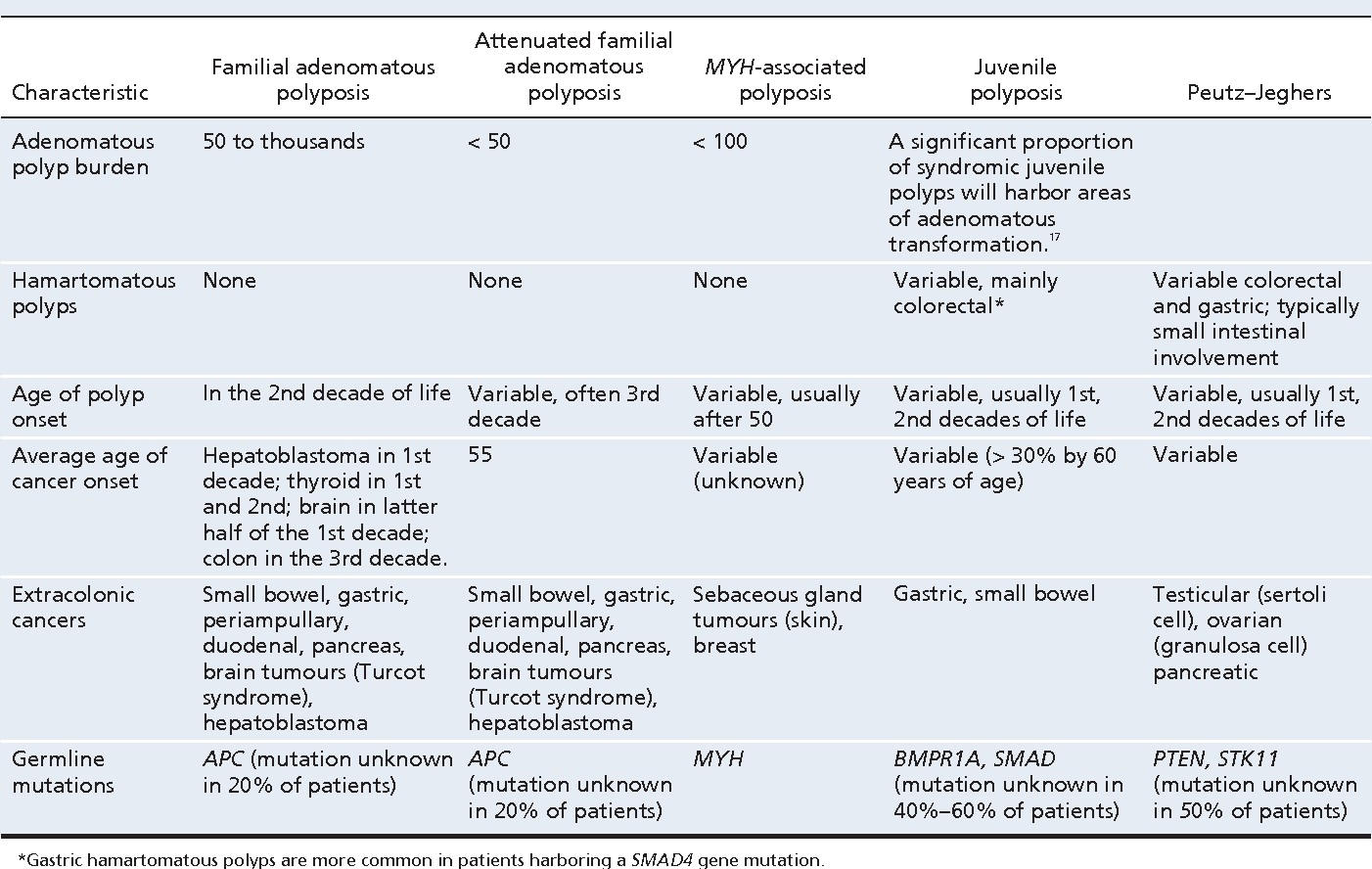
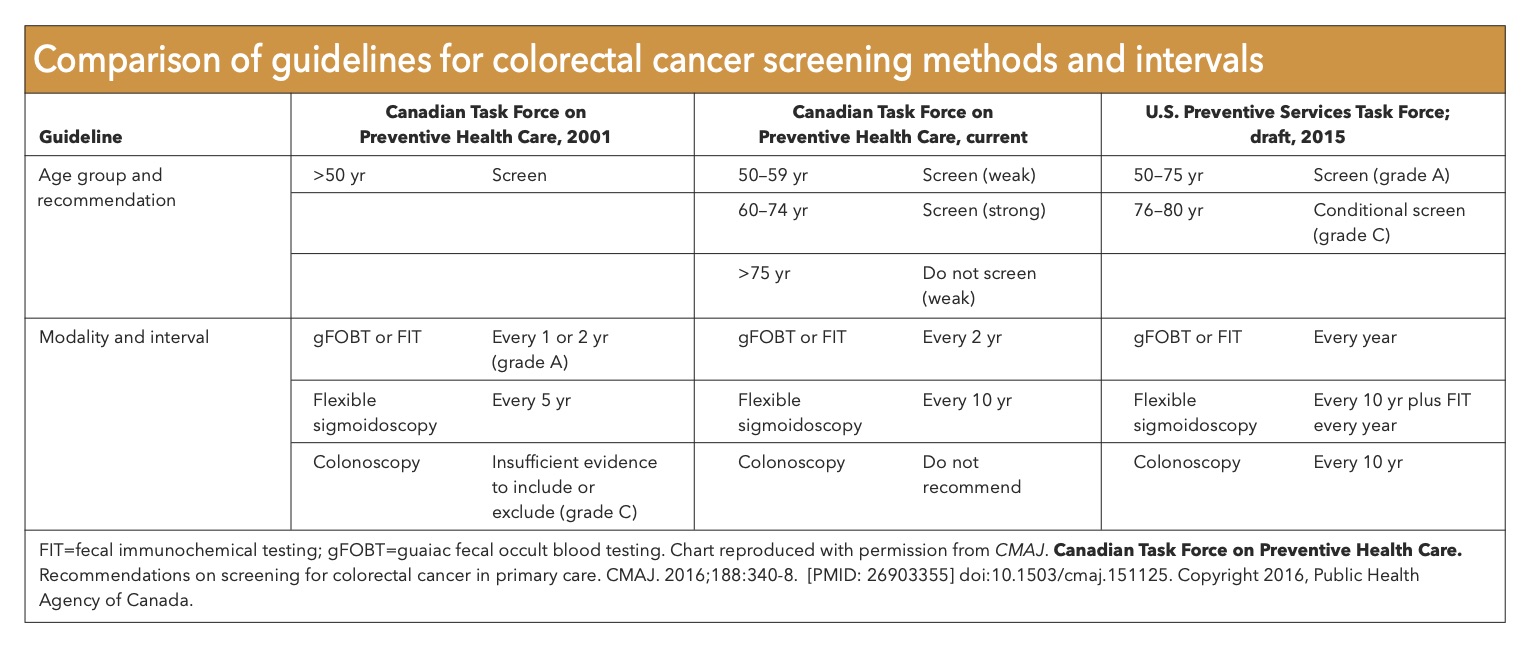
1-3 Familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis AFAP account for about 1 as does MYH-associated polyposis MAP4-6. 4 5 10 18 Therefore followup by colonoscopy from the teenage years onwards and preventive proctocolectomy are recommended to patients. Along with the risk for CRC both syndromes are associated with elevated risk for other tumors.
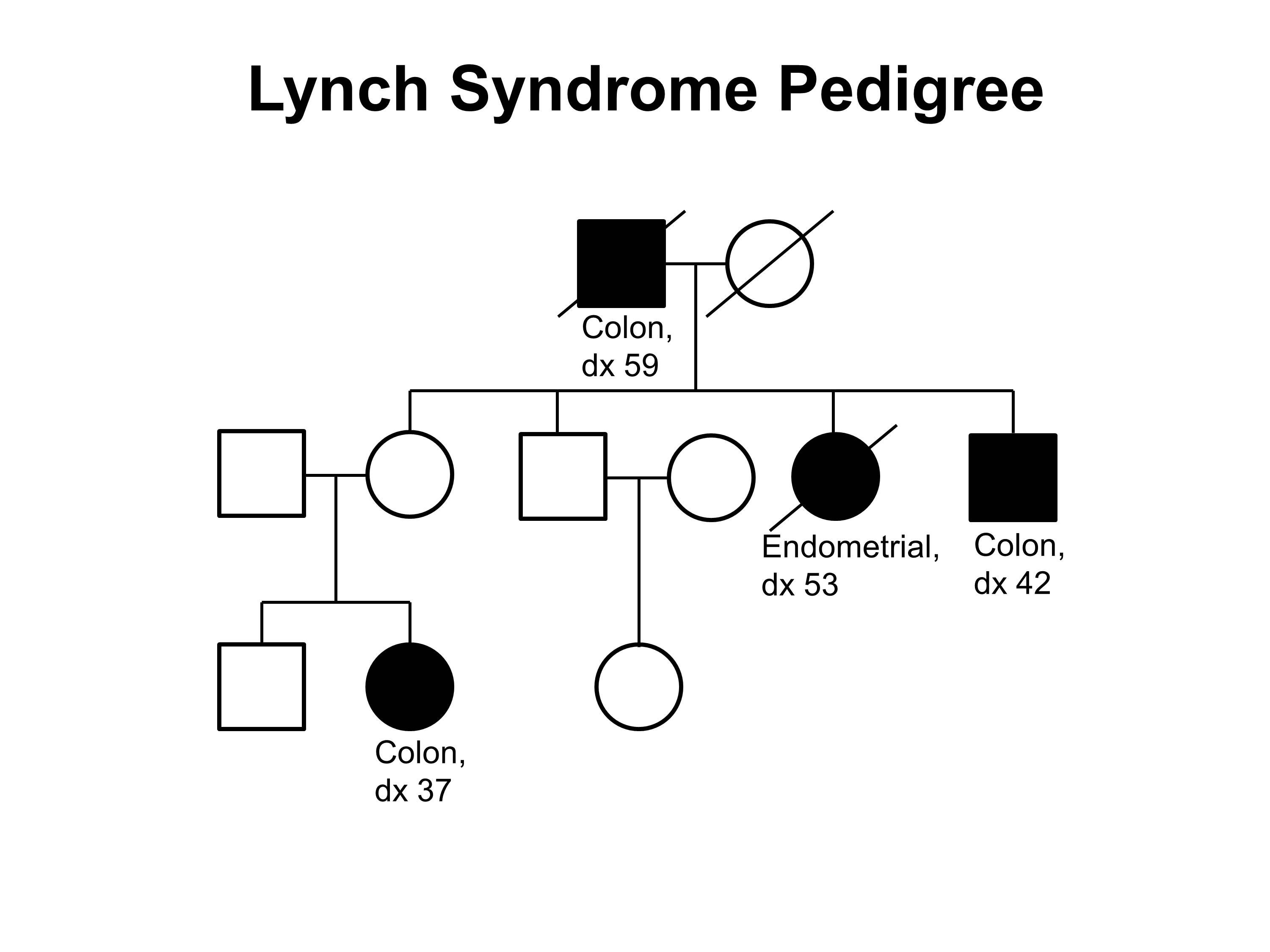
Lynch syndrome LS Overview and clinical presentation. MUTYH-associated polyposis MAP vs. Two major autosomal dominant forms of heritable CRC are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and Lynch syndrome also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.
Familial adenomatous polyposis is a hereditary disease caused by mutations of APC. Microsatellite instability is discussed both as a predictor of treatment effectiveness and as a predictor of Lynch syndrome. 15thAnnual West Coast Colorectal Cancer Symposium Oct.
Familial colorectal cancer CRC accounts for 10 to 20 of all cases of CRC. The most frequent hereditary colorectal cancer CRC syndromes are Lynch syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis FAP accounting for approximately 5 of the CRC burden. Both are characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of transmission and require an individualized approach of intensified screening and prophylactic surgery.
Three of the most common are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC known as Lynch syndrome and MYH-associated Polyposis MAP. Both arise from germline mutations that result in destabilization and deregulation of cell growth. Samadder shares information about Lynch syndrome LS familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and attenuated FAP AFAP to provide clinicians with tools to understand the genetic bases of these conditions and the appropriate diagnosis and management.
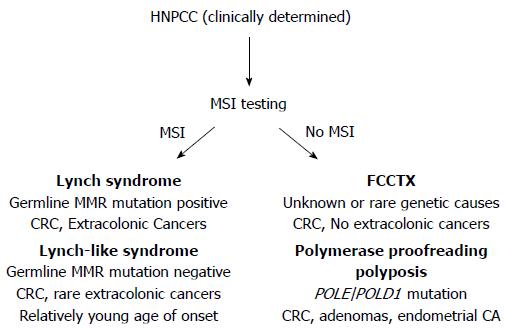
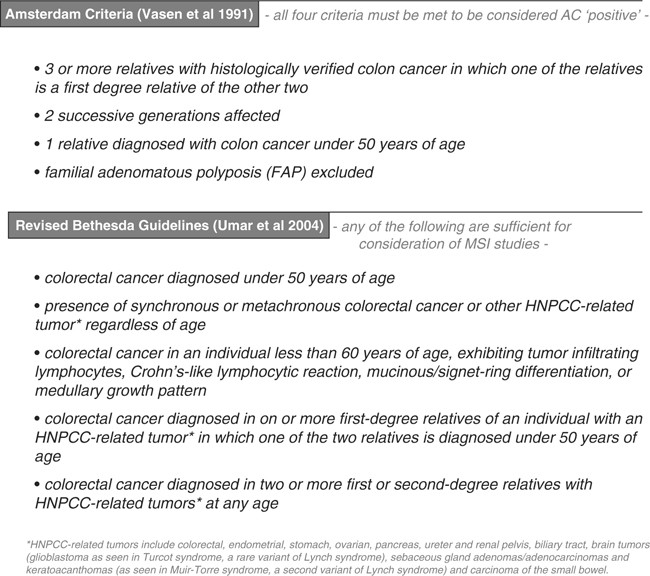
Conversely many families that have Lynch syndrome do not meet these criteria. This report does not cover other interventions eg.
Familial colorectal cancer CRC accounts for 10 to 20 of all cases of CRC.
Three of the most common are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC known as Lynch syndrome and MYH-associated Polyposis MAP. 4 5 10 18 All patients with FAP are considered to have had CRC at some point during their lifetime unless they have received any treatment for adenomatous polyposis. Two major autosomal dominant forms of heritable CRC are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and Lynch syndrome also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Two major autosomal dominant forms of heritable CRC are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and Lynch syndrome also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Tumors should be verified by pathologic examination. Three of the most common are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC known as Lynch syndrome and MYH-associated Polyposis MAP. Microsatellite instability is discussed both as a predictor of treatment effectiveness and as a predictor of Lynch syndrome. Conversely many families that have Lynch syndrome do not meet these criteria. Patients with familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and patients with Lynch syndrome have an increased risk of developing small intestinal neoplasia.
Familial colorectal cancer CRC accounts for 10 to 20 of all cases of CRC. Whether testing begins with adenomatous polyposis coli APC mutations or screening for mismatch. In this article Dr. Familial adenomatous polyposis should be excluded. Surgical Treatment of Patients with Lynch Syndrome Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. More specifically Lynch syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis FAP. MUTYH-associated polyposis MAP vs.


























Post a Comment for "Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Vs Lynch Syndrome"