What Is The Correct Frequency Of Disease Occurrence Measured By A Cohort Study?
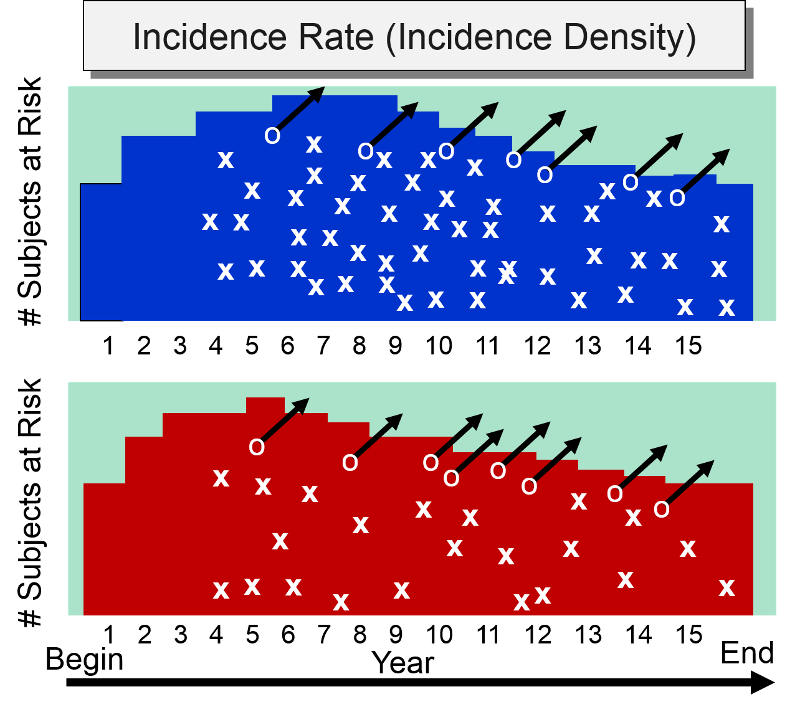
What is the correct frequency of disease occurrence measured by a cohort study?. Suppose a case-control study were conducted in which cardiac patients who recently died of their heart disease were compared to control cardiac patients with similar disease who survive. The measure of disease in cohort studies is the incidence rate which is the proportion of subjects who develop the disease under study within a specified time period. A measure of the association between frequency of exposure and frequency of outcome used in case-control studies.
There is a 50 reduction in disease in the exposed group. A measure of disease occurrence. 10 lost to follow-up.
Summary measure of the frequency of exposure for each study unit eg per capita cigarette consumption Summary measure of the frequency of outcome for each study unit eg CHD mortality Joint distribution of exposure and disease. Assume such a study had found that 40 of the recent cardiac deaths were taking calcium channel blockers at the time of death as compared to 25 of the controls. A The tea drinkers have lower risk of developing diabetes.
Incidence is best understood in the context of prospective cohort studies Chapter 1 Section 141. The number of persons in. The study followed 5000 healthy adults every 2 years for over 50 years it was considered an excellent study because the investigators could identify a large enough number of people who both had and did not have risk factors for heart disease the study was so successful it was eventually expanded to include other causes and other diseases.
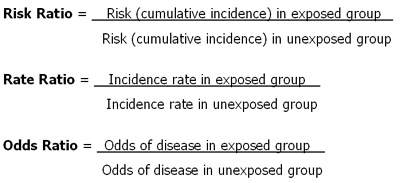
For example if a cohort study was done and investigators observed an incidence in the exposed of 1 per 1000000 in 20 years and an incidence in the unexposed and an incidence in the unexposed of 2 per 1000000 in 20 years the RR would be 05. To assess the effect of a risk factor comparisons are made between for example disease frequency in people who have been exposed to that risk factor and disease frequency in those who have not been exposed to that risk factor. In a historical cohort study the data concerning exposure and occurrence of a disease births a political attitude or any other categorical variable are collected after the events have taken place and the subjects those exposed and unexposed to the agent under study are assembled from existing records or.
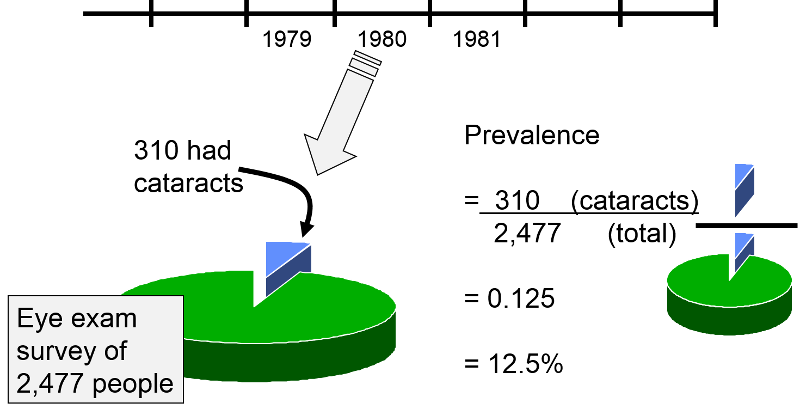
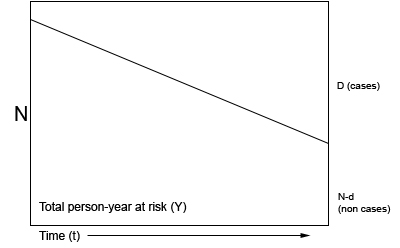
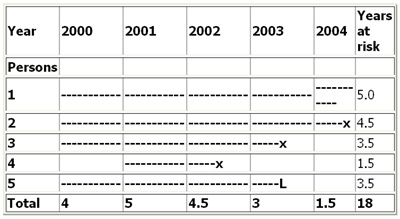
The total number of individuals who have an attribute or disease at a particular time or period divided by the population at risk of having the disease at that time or midway through the period. 2 new cases of eye disease detected out of 80. The numerator of the rate is the number of diseased subjects and the denominator is.
In the above example the incidence rate for disease X is calculated as. The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a case-control study see Lesson 1.
A case-control study is based on enrolling a group of persons with disease case-patients and a comparable group without disease controls.
Summary measure of the frequency of exposure for each study unit eg per capita cigarette consumption Summary measure of the frequency of outcome for each study unit eg CHD mortality Joint distribution of exposure and disease. The study followed 5000 healthy adults every 2 years for over 50 years it was considered an excellent study because the investigators could identify a large enough number of people who both had and did not have risk factors for heart disease the study was so successful it was eventually expanded to include other causes and other diseases. The total number of individuals who have an attribute or disease at a particular time or period divided by the population at risk of having the disease at that time or midway through the period. In the above example the incidence rate for disease X is calculated as. There is a 50 reduction in disease in the exposed group. Instead the risk of an outcome associated with an exposure is calculated the odds of exposure among the cases and controls. To assess the effect of a risk factor comparisons are made between for example disease frequency in people who have been exposed to that risk factor and disease frequency in those who have not been exposed to that risk factor. The measure of disease in cohort studies is the incidence rate which is the proportion of subjects who develop the disease under study within a specified time period. The number of persons in.
The OR is called an indirect measure of risk between incidence rates have not been used. The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a case-control study see Lesson 1. The OR is called an indirect measure of risk between incidence rates have not been used. So a VE of 90 indicates a 90 reduction in disease occurrence among the vaccinated group or a 90 reduction from the number of cases you would expect if they have not been vaccinated. In a cohort study the risk ratio of developing diabetes was 086 when comparing consumers of tea the exposed to those who did not drink tea the unexposed. Measures of disease occurrence may also be used to study the risk factors or causes of disease. For example if a cohort study was done and investigators observed an incidence in the exposed of 1 per 1000000 in 20 years and an incidence in the unexposed and an incidence in the unexposed of 2 per 1000000 in 20 years the RR would be 05.
































Post a Comment for "What Is The Correct Frequency Of Disease Occurrence Measured By A Cohort Study?"